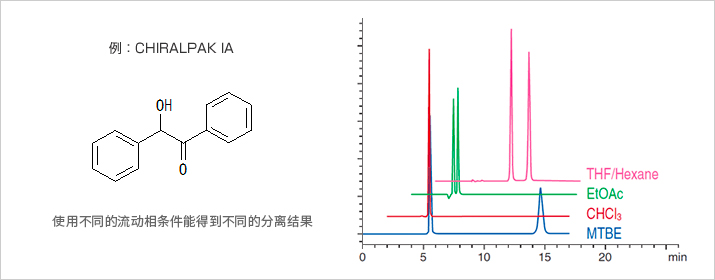
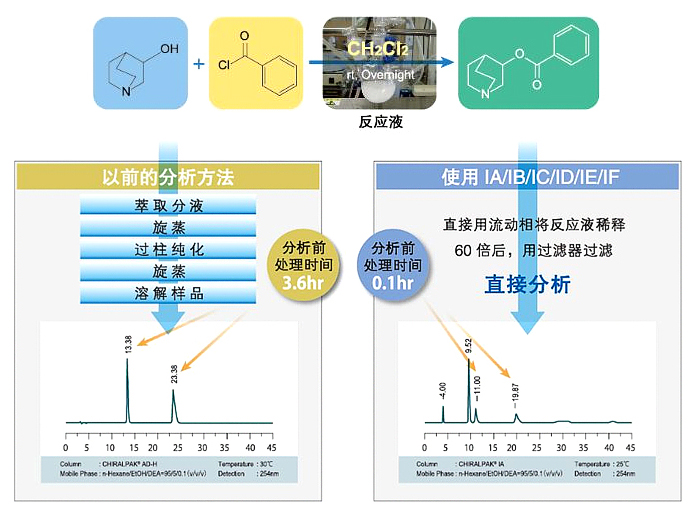
正己烷 (n-Hexane)
二甲基亞砜 (DMSO)
異丙醇 (IPA)
氯仿 (Trichloromethane)
甲基叔丁基醚 (MTBE)
乙腈 (Acetonitrile)
二氯甲烷 (Dichloromethane)
甲苯 (Methylbenzene)
四氫呋喃 (THF)
1,4-二氧六環(huán)(1,4-dioxane)
乙酸乙酯 (Acetic ether)
水 (H2O)
正己烷 (n-Hexane)
二甲基亞砜 (DMSO)
異丙醇 (IPA)
氯仿 (Trichloromethane)
甲基叔丁基醚 (MTBE)
乙腈 (Acetonitrile)
二氯甲烷 (Dichloromethane)
甲苯 (Methylbenzene)
四氫呋喃 (THF)
1,4-二氧六環(huán)(1,4-dioxane)
乙酸乙酯 (Acetic ether)
水 (H2O)